Fantasy forecasting and the ECB
The ECB under former President Jean-Claude Trichet twice raised interest rates into oncoming recessions (in 2008 and 2011). The current ECB hasn’t raised rates yet but is scaling back QE much faster than was expected late last year.
The six-month rate of change of Eurozone real narrow money had turned negative before the 2008 / 2011 rate rises and subsequent recessions. It is about to do so again now.
In an eerie replay, M. Trichet yesterday gave an interview in which he opined that the Eurozone was “far from recession territory”.
The current ECB seems equally complacent. The staff forecast for GDP growth in 2022 was yesterday lowered from 4.2% to 3.7% but still incorporates quarterly increases of 1.0% in Q2 and Q3, i.e. a combined 2.0% or 4% annualised.
The “best” monetary leading indicator of Eurozone GDP, according to the ECB’s own research, is real non-financial M1, i.e. holdings of currency and overnight deposits by households and non-financial corporations deflated by consumer prices.
The six-month change in real non-financial M1 fell to zero in January and is likely to have been negative in February, based on a further increase in six-month consumer price momentum – see chart 1.
Chart 1
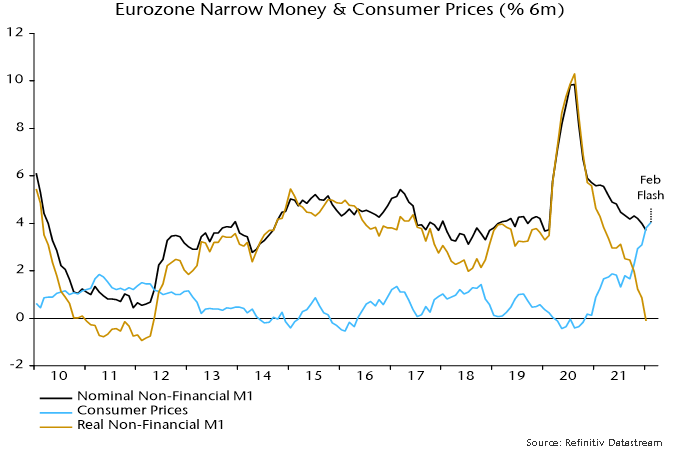
The six-month real narrow money change was negative in 18% of months between 1970 and 2019. The average change in GDP in the subsequent two quarters combined was zero. The average since the inception of the euro in 1999 was -0.8%.
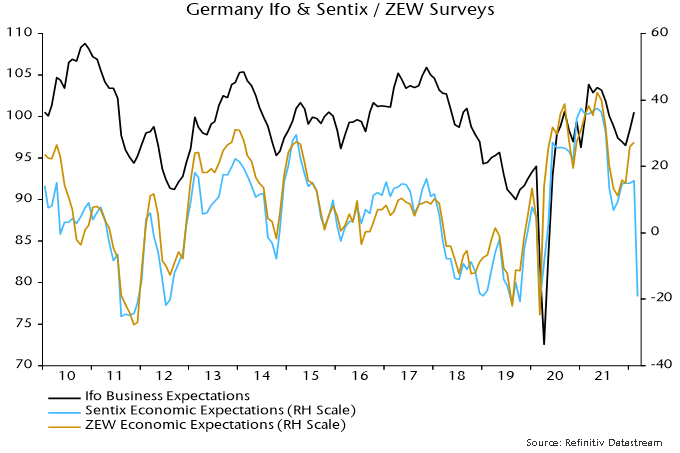
Business surveys could be about to crater: the March Sentix survey of financial analysts is ominous – chart 2. The ECB and consensus may portray weakness as a kneejerk response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, drawing a parallel with past geopolitical events that had little lasting economic impact. Monetary trends suggest that a slowdown to stall speed was already in prospect and the Ukraine shock may tip the economy over into recession.
Chart 2
The ECB is in a policy bind of its own making. The view here is that it is too late to tighten and policy-makers should ride out the current inflation storm. The worry is that inflation expectations will become “unanchored”. Fake hawkish rhetoric backed by fantasy GDP forecasts may be their attempted escape route.

Reader Comments (3)
Some people say the ECB has lost all credibility as a price stability targeting bank since, as you say, they are left with fantasy forecasts to justify not tightening. But surely the bigger story is that they are nnot independent of the desire to print money to address every problem - real or imagined. Climate change? Print money. Inequality = print money. Energy shortage = print money. Sudden realisation of the need to defend oneself = definitely print money. No understanding that the money printing is the cause of the problem!
Whist I accept and agree with your analysis ,I am convinced that #ZNIRP is "contractionary" medium/long run .The exit of low policy rates will re-balance the level of MV that goes into assets and GDP transactions (your work on QT of wealth supports this) actually supporting CPI .
There will be turmoil and perhaps the need for more QE during the process ,but if low or negative policy rates are maintained #Japanification and the stagnation that goes with it will be the result . Banks (the more efficient money creators ) can't support credit creation sufficiently at these low policy rates.
Lastly when Trichet hiked in 11 M3 was still growing sufficiently . There is no good time to exit #ZNIRP but anytime is the right time
Thank you for the comments. Tim - I agree with the aim but rates should be raised when money growth is rising and the stockbuilding cycle is in an upswing. There have been three major opportunities over the last decade, which were effectively declined.